Global
Ten Youngest Countries in the World
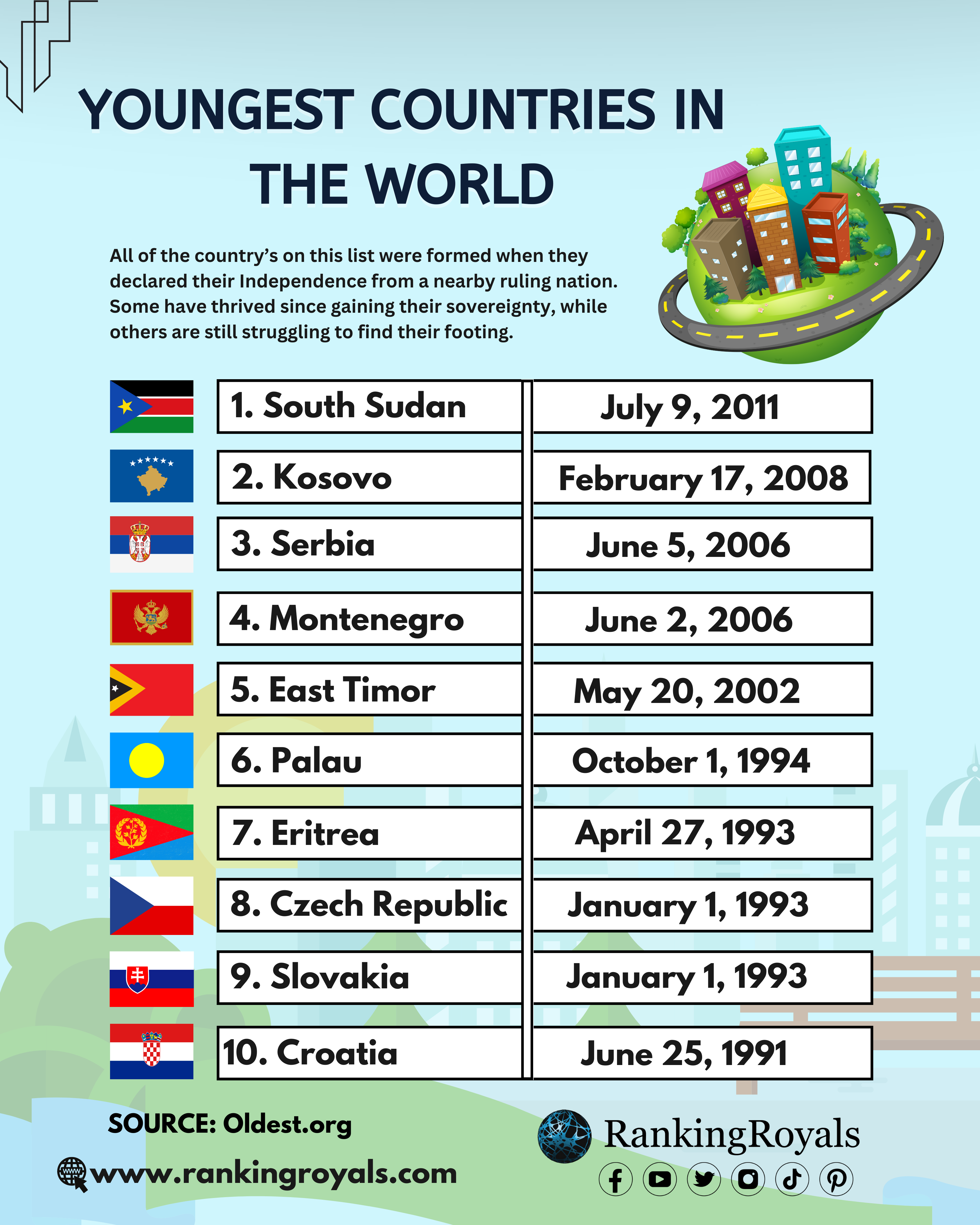
At present, 196 countries are recognized around the world. Many countries have existed for a long time, but new countries are still emerging in the modern era. Actually, all of the youngest countries in the world on this list are only several decades old. In 2021, the top-ranked and youngest country on this list celebrated the 10th anniversary of its founding.
Almost every country on this list was formed when they proclaimed their independence from a nearby ruling nation. Some have flourished since the gain of sovereignty, while others are struggling to make up for it.
The following are the 10 youngest countries in the world:
1. South Sudan
Year of Independence: July 9, 2011
Capital: Juba
Government Type: Federal Presidential Constitutional Republic
Population: 12,778,250 (2022 Estimate)
On July 9, 2011, South Sudan declared independence from Sudan, making it the youngest country in the world. The country is situated in the East African region.
South Sudan has had a lengthy history of occupation since its creation as the former part of Sudan. From 1899 to 1956, Sudan was ruled by the United Kingdom and Egypt. Unfortunately, following Sudanese independence, two civil wars broke out. From 1972 to 1983, the first civil war in Sudan took place. The second Sudanese civil war immediately followed the first and did not end until 2005. At that time, after the establishment of an autonomous government for Southern Sudan, Southern autonomy was restored.
In 2011, South Sudan became fully independent and was an officially recognized member of the United Nations.
Did You Know?
As of 2019, South Sudan is ranked third-least happy in the most recent UN World Happiness Report, third-least peaceful in the Global Peace Index, and fourth-most fragile in the American Funds for Peace’s Fragile States Index.
2. Kosovo
Year of Independence: February 17, 2008
Capital: Pristina
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 1,770,436 (2022)
Another country that has declared independence in the last few decades is Kosovo, officially the Republic of Kosovo. Kosovo declared its independence from neighboring Serbia on February 17, 2008. However, Serbia does not recognize Kosovo as an independent country, and only 97 out of 193 (50.26%) United Nations member states have formally recognized Kosovo.
Kosovo was ruled by several empires, including Romans, Byzantines, Bulgarians, Serbians, and Ottomans, during the ancient period. Kosovo has experienced strong economic growth by international financial institutions in the last decade.
Did You Know?
Kosovo has about 1.9 million inhabitants, of which 95 percent are ethnic Albanians.
3. Serbia
Year of Independence: June 5, 2006
Capital: Belgrade
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 7,221,365 (2022)
In 2006, Serbia gained independence from Montenegro when it peacefully broke up the country’s federation. Since 1918, the country has not been an autonomous state. Serbia has a rich history dating back to the Paleolithic era, with its territory inhabited at that time.
During the Great Migrations of the 6th and 7th centuries, Serbians moved to the Balkans region along with various South Slavic tribes.
The Serbian Empire was founded in the 14th century, but it lasted only a short time. The Empire ended in 1371 with Uroš V’s death and after the Serbian state broke up.
Between the 16th and early 19th centuries, Serbia was a part of the Ottoman Empire. The Serbian Revolution formed the nation-state as the first democratic monarchy in the area at the beginning of the 19th century.
Serbia and other South Slavic states formed Yugoslavia after the Second World War.
Did You Know?
Serbia is an economically prosperous country with 64th place and a “very high” score on the Human Development Index.
4. Montenegro
Year of Independence: June 2, 2006
Capital: Podgorica
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 627,082 (2022)
Montenegro is another young country to break ties with Serbia in order to become a sovereign state of its own. Montenegro became a kingdom at the beginning of the 20th century, but it was a part of Yugoslavia after World War I.
Montenegro and Serbia have formed a federation since Yugoslavia broke up in the 1990s. In 2006, following the independence declaration of Montenegro, the Confederation was peacefully abolished.
In the King Milutin Charter of 1276, Montenegro, first time ever in its history, is referred to as “Crna Gora” The country’s name comes from the dark, dense trees that cover Mount Lovcen and the surrounding region, giving them the appearance of being “black.”
Did You Know?
Montenegro is a founder of the Union for the Mediterranean and currently pursuing its membership in the European Union.
5. East Timor
Year of Independence: May 20, 2002
Capital: Dili
Government Type: Unitary Semi-Presidential Constitutional Republic
Population:1,341,296 (2022)
East Timor, commonly known as the Democratic Republic of Timor-Leste, is an island nation in Southeast Asia. It is composed of the eastern half of the island of Timor, the nearby islands of Atauro and Jaco, and Oecusse, an exclave on the island’s western edge, which is surrounded by Indonesia’s West Timor.
In fact, the Portuguese seized East Timor in the 16th century, and they ruled over it until 1975. That year East Timor declared its independence, but the country was immediately attacked by a neighboring Indonesian.
During the violent Indonesian colonization of East Timor, several thousand Timorese people died. With the help of the UN, this conflict began to end in 1999.
Did You Know?
East Timor is the only Asian country in the Southern Hemisphere.
6. Palau
Year of Independence: October 1, 1994
Capital: Ngerulmud
Government Type: Unitary Presidential Constitutional Republic under a Non-Partisan Democracy
Population: 18,055 (2022)
Palau, officially called the Republic of Palau, is an island country in the western Pacific. During the 16th century, unlike many Pacific island nations, Palau was colonized by Europeans.
The Palauan islands were first colonized by Spain, who joined them in the Spanish East Indies in 1574. Palau was sold to Germany after Spain was defeated in the Spanish-American War of 1898.
The Islands became part of Japan’s South Sea Mandate after the First World War by the League of Nations. The US government had taken control of Palau after the end of World War II.
In 1994, after decades of being a territory of the United States, Palau was granted full sovereignty through an agreement with the US on free association.
Did You Know?
Because of its history of colonization, Palau is a melting pot with two official languages, Palauan and English. Sonsorolese, Japanese, and Tobian are recognized as regional languages.
7. Eritrea
Year of Independence: April 27, 1993
Capital: Asmara
Government Type: Unitary One-party Presidential Republic under a Totalitarian Dictatorship
Population: 3,684,032 (2022)
Eritrea is a nation within the Horn of Africa region, formally known as The State of Eritrea. The Eritrean War of Independence lasted for 30 years until Eritrea achieved full de facto independence in 1991. In 1993, Eritrea attained de jure independence on the basis of a referendum.
The Ottomans occupied much of the North Eastern part of today’s Eritrea for many decades in the 16th century. The 1st Europeans to reach the region were the Portuguese, but Eritrea was not colonized by them.
Italy set up a new colony of Italian Eritrea by the end of the 19th century, and it is part of the Kingdom of Italy. The British expelled the Italians from Eritrea during the Second World War, from Eritrea. In the early 1950s, Eritrea was federated with Ethiopia on the orders of the US Government despite the wishes of its own people.
Did You Know?
The country has never held national legislative and presidential elections, even though Eritrea is technically a unitary one-party republic. Since 1993, when Eritrea became an official independent country, Isaias Afwerki has served as president.
8. Czech Republic
Year of Independence: January 1, 1993
Capital: Prague
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 10,500,207 (2022)
In 1993, after Czechoslovakia’s separation, the Czech Republic, usually referred to as Czechia, was formed. Czechia is one of the many countries in this part of Europe that has been ruled by different empires.
The Czech Republic was regarded as an imperial country of the Holy Roman Empire in the 11th century when it belonged to the Duchy of Bohemia. The Czech Republic had become part of the Austrian Empire following the collapse of the Holy Empire in 1806.
In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, Nazi Germany seized control of the Czech territories. After being restored in 1945, Czechoslovakia transformed into an Eastern Bloc communist state in the aftermath of a coup in 1948.
During the Prague Spring in 1968, the Czechs attempted to take down communist power but were unsuccessful. It took until the Velvet Revolution in 1989 for communism to be abolished.
Did You Know?
The Czech Republic is the 9th safest and most peaceful country and 31st in democratic governance.
9. Slovakia
Year of Independence: January 1, 1993
Capital: Bratislava
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 5,643,453 (2022)
Slovakia is the other half of the former Czechoslovakia, which gained its sovereignty along with the Czech Republic in 1993. Czechoslovakian was founded in the aftermath of World War I when Austria and Hungary ceased to exist.
During the interwar period, it was the only country in Eastern and Central Europe to remain a democracy. Unfortunately, fascist regimes gradually took control of Czechoslovakia. Czechoslovakia, after a coup in 1948, was governed by the Communists and joined the Soviet-led Eastern Bloc.
Slovakia, since its independence, has become a developed country with an advanced high-income economy which is very significant in the index of human development. The assessments of civil liberties, press freedoms, Internet freedom, democratic governance, and peacefulness also show good results in Slovakia.
Did You Know?
Slovakia is the largest per capita car manufacturer in the world, with 1.1 million vehicles manufactured in 2019, amounting to 43 % of its total industrial production.
10. Croatia
Year of Independence: June 25, 1991
Capital: Zagreb
Government Type: Unitary Parliamentary Constitutional Republic
Population: 4,030,358 (2022)
The Republic of Croatia, known as Croatia, is a nation in Southeast Europe. Croatia declared independence on June 25, 1991, after the termination of its association with Yugoslavia. But for four years during the War of Independence, Croatia continued to fight for its independence.
After the end of the war, Croatia launched a series of large offensives named Operation Flash and Operation Storm in 1995. The two governments of Serbia and Croatia have worked together for most of the time. Although Croatia had to face the challenges of postwar reconstruction, it was a long way from here.
Did you know?
Currently, Croatia has been classified as a wealthy country by the World Bank and is highly ranked on the Human Development Index. In addition, Croatia is a popular destination for tourists.
Read More: Oldest Living People in the World 2023





































