Infographics
Military Spending By Country (Top 144 Countries)
Military spending by country refers to the amount of money allocated to a nation’s armed forces, which may include personnel, equipment, and operations funding. This expenditure can have significant effects on a nation’s economic and political stability, as well as its international relations. As a result, many nations invest heavily in their military to defend their borders and project their influence. In contrast, others prioritize non-military expenditures such as social programs and infrastructure development.
In recent years, military expenditures have become a topic of increasing global interest, particularly as international tensions and security concerns have increased. Some countries that spend the most on their military are the United States, China, and Russia. Other countries, like Japan and Germany, have solid military powers but choose to spend less on defense.
Facts about Military Spending by Country
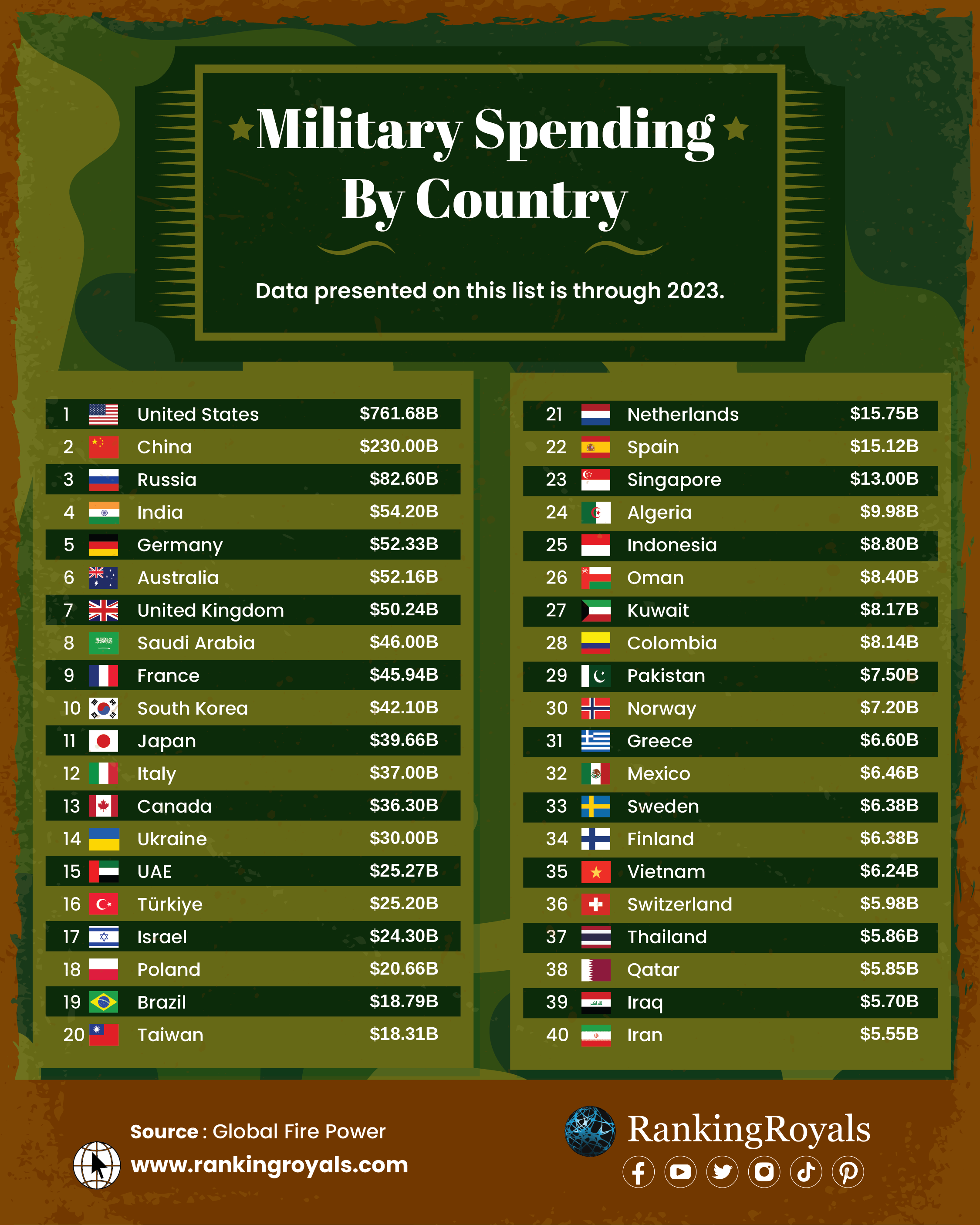
- The USA spends more on its defense than any other country. It spent about US$761.68 billion on its military in 2023, about 38% of the total amount spent on the military worldwide. The country spends more on its defense than the following ten countries combined.
- China ranks second in the globe in terms of military expenditures. It spent approximately US$230 billion on its military, representing about 12% of the world’s total military spending.
- The United States and China spent nearly half of the world’s military expenditure.
- In 2021, global military expenditures as a percentage of global GDP reached 2,2%, 0.1 percentage points lower than in 2020.
- Oman spends the most on its defense as a share of its GDP. In 2021, it spent about 7.34 percent of its GDP on its defense. Kuwait spent 6.69 % Saudi Arabia spent 6.59 %, and Algeria spent 5.59 %.
- The USA has a limited amount of defense spending per person. Instead, Qatar and Israel spend more on their defense per person than the US.
- About 71% of all military spending in the world is done by the ten countries that spend the most on their military.
- In 2023, global military spending will be approximately $1.99 trillion.
- Some countries, such as Costa Rica, have no military spending and have abolished their armed forces.
- Geopolitical factors like regional security risks, territorial disputes, and alliances often affect how much money is spent on the military.
- Spending on the military can have big effects on the economy and society. It can change a country’s budget imbalance, debt, and inflation. Also, spending on the military can take money away from social programs like schooling and health care.
- Due to the need to maintain national security and reconstruct infrastructure devastated by war, countries in conflict or post-conflict situations often have high military expenditures.
- Military spending can also affect foreign relations because it can show how powerful and influential a country’s military is.
How has military spending changed over time?
Since 1990, when the Cold War ended, both the amount the government spends on defense and the economy’s total output (GDP) has gone down. This has made it possible for the government to spend money on things like schooling, health care, and building up the country. In 2019, governments worldwide spent an average of 6.5% of their budgets on the military. Based on unweighted country averages, worldwide military spending has dropped by almost half, from 3.6% of GDP during the Cold War (from 1970 to 1990) to 1.9% of GDP in the years after the global financial crisis (from 2010 to 2019). In 2021, all countries provided their armies with an average of 5.9% of their total budgets. This is the same as in 2020, but it is less than the 6.4% they gave in 2012. Even though the world average tends to be down, the trends in different regions vary.
How does military spending vary across different regions of the world?
The average proportion in European countries increased by 0.1 percentage points in 2021 compared to the previous year, while the average share in the Americas remained unchanged. In 2021, countries in the Americas (4%) and Europe (4.7%) allocated the fewest percentages of their government spending to the military. Africa allocated an average of 6.1% of its government budget to the military (0.3 percentage points less than in 2020), while Asia and Oceania allocated an average of 6.7% (0.2 percentage points more than in 2020). Middle Eastern countries gave 12 percent of their government budgets to the military, the highest average proportion of all world regions. However, this is a decrease of 0.3 percentage points compared to 2020.
How does military spending impact a country’s economic growth and development?
Depending on various aspects, such as the size of the military budget, the level of economic development, and the allocation of resources, military expenditure can positively and negatively affect a country’s economic growth and development.
On the one hand, military spending can contribute to economic growth by stimulating demand for goods and services and generating jobs. On the other hand, government tax revenue can be generated due to the economic activity stimulated by military contracts to the manufacturing sector and other related industries.
On the other hand, excessive military expenditure can divert resources from other areas that may be more beneficial for long-term economic growth and development, such as education, healthcare, and infrastructure. In addition, excessive military spending can result in budget deficits, inflation, and a decline in the currency’s value.
Let’s explore some frequently asked questions about the military and its spending.
What is the most powerful military in the world?
The United States military is regarded as the strongest military in the world due to its advanced weaponry, higher training, and cutting-edge technology.
What is the largest military in the world?
China’s People’s Liberation Army has approximately 2 million active personnel, making it the largest military globally.
Who are the largest arms producers?
Lockheed Martin, Boeing, Northrop Grumman, Raytheon Technologies, and General Dynamics are among the world’s top five biggest arms manufacturers. All of these companies are based in the United States. These businesses make various weapons and military gear, such as fighter jets, missiles, drones, tanks, etc.
The global arms business is worth billions of dollars, and the biggest arms makers have a lot of power and impact at home and worldwide.
What does NATO do around the world?
NATO is an organization of North American and European countries that work together politically and militarily to protect each other from possible threats.
What is the role of the United Nations in military conflicts?
In certain circumstances, the United Nations can authorize using military force, such as in self-defense or safeguarding civilians from harm. In addition, UN peacekeeping missions are also deployed in conflict zones to help maintain peace and stability.
What are some of the benefits of serving in the military?
Education and training opportunities, health care, housing allowances, retirement benefits, and the chance to travel and acquire life experience are among the advantages of military service.
Why do countries spend so much money on their military?
Countries spend money on their military for many reasons, including national security, defense against possible threats, and showing power and influence in international issues.
What is the role of the military-industrial complex in military spending?
The military-industrial complex is the close link between the military and the defense industry, often leading to the development and purchase of expensive weapons systems and technology. This can make a strong case for spending more money on the military, even when it might not be necessary or effective.
What is the role of military intelligence?
Military intelligence is in charge of gathering and analyzing information important to national security, such as the skills and plans of the enemy, changes in geopolitics, and new threats.
What is a military alliance?
A military partnership is an agreement between two or more countries to defend and protect each other by working together.
Here is a list of Military spending By Country according to Global Fire Power (GFP):
| Rank | Country | Defense Budgets |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | $761.68B |
| 2 | China | $230.00B |
| 3 | Russia | $82.60B |
| 4 | India | $54.20B |
| 5 | Germany | $52.33B |
| 6 | Australia | $52.16B |
| 7 | United Kingdom | $50.24B |
| 8 | Saudi Arabia | $46.00B |
| 9 | France | $45.94B |
| 10 | South Korea | $42.10B |
| 11 | Japan | $39.66B |
| 12 | Italy | $37.00B |
| 13 | Canada | $36.30B |
| 14 | Ukraine | $30.00B |
| 15 | United Arab Emirates | $25.27B |
| 16 | Turkiye | $25.20B |
| 17 | Israel | $24.30B |
| 18 | Poland | $20.66B |
| 19 | Brazil | $18.79B |
| 20 | Taiwan | $18.31B |
| 21 | Netherlands | $15.75B |
| 22 | Spain | $15.12B |
| 23 | Singapore | $13.00B |
| 24 | Algeria | $9.98B |
| 25 | Indonesia | $8.80B |
| 26 | Oman | $8.40B |
| 27 | Kuwait | $8.17B |
| 28 | Colombia | $8.14B |
| 29 | Pakistan | $7.50B |
| 30 | Norway | $7.20B |
| 31 | Greece | $6.60B |
| 32 | Mexico | $6.46B |
| 33 | Sweden | $6.38B |
| 34 | Finland | $6.38B |
| 35 | Vietnam | $6.24B |
| 36 | Switzerland | $5.98B |
| 37 | Thailand | $5.86B |
| 38 | Qatar | $5.86B |
| 39 | Iraq | $5.70B |
| 40 | Iran | $5.55B |
| 41 | Belgium | $5.51B |
| 42 | Romania | $5.15B |
| 43 | Chile | $5.06B |
| 44 | Portugal | $4.91B |
| 45 | North Korea | $4.50B |
| 46 | Hungary | $4.50B |
| 47 | Egypt | $4.36B |
| 48 | Philippines | $4.28B |
| 49 | Denmark | $4.20B |
| 50 | Bangladesh | $3.89B |
| 51 | New Zealand | $3.80B |
| 52 | Libya | $3.57B |
| 53 | Nigeria | $3.48B |
| 54 | Austria | $3.43B |
| 55 | Czechia | $3.26B |
| 56 | Azerbaijan | $3.10B |
| 57 | Argentina | $3.06B |
| 58 | Cuba | $2.99B |
| 59 | South Africa | $2.81B |
| 60 | Kazakhstan | $2.62B |
| 61 | Malaysia | $2.59B |
| 62 | Myanmar | $2.29B |
| 63 | Ecuador | $2.27B |
| 64 | Slovakia | $2.09B |
| 65 | Syria | $2.02B |
| 66 | Venezuela | $1.93B |
| 67 | Jordan | $1.90B |
| 68 | Peru | $1.85B |
| 69 | Bahrain | $1.54B |
| 70 | Ireland | $1.26B |
| 71 | Kenya | $1.19B |
| 72 | Tunisia | $1.18B |
| 73 | Lithuania | $1.15B |
| 74 | Sri Lanka | $1.11B |
| 75 | Bulgaria | $1.11B |
| 76 | Uruguay | $1.07B |
| 77 | Angola | $1.06B |
| 78 | Serbia | $1.06B |
| 79 | Croatia | $1.05B |
| 80 | Morocco | $1.04B |
| 81 | Yemen | $1.01B |
| 82 | Lebanon | $1.00B |
| 83 | Uganda | $934.25M |
| 84 | Latvia | $927.47M |
| 85 | Tanzania | $748.92M |
| 86 | Panama | $741.16M |
| 87 | Belarus | $723.12M |
| 88 | Estonia | $713.69M |
| 89 | Uzbekistan | $692.52M |
| 90 | Armenia | $632.50M |
| 91 | Cambodia | $632.25M |
| 92 | Dominican Republic | $630.72M |
| 93 | Luxembourg | $600.00M |
| 94 | Mali | $591.26M |
| 95 | Slovenia | $581.68M |
| 96 | Ethiopia | $538.00M |
| 97 | Ivory Coast | $510.00M |
| 98 | Bolivia | $476.97M |
| 99 | Botswana | $473.40M |
| 100 | Nepal | $437.58M |
| 101 | Burkina Faso | $434.25M |
| 102 | Turkmenistan | $407.07M |
| 103 | Honduras | $405.11M |
| 104 | Cameroon | $398.00M |
| 105 | Guatemala | $388.00M |
| 106 | Namibia | $363.80M |
| 107 | Paraguay | $353.00M |
| 108 | Congo | $348.16M |
| 109 | Senegal | $345.38M |
| 110 | DR Congo | $299.22M |
| 111 | El Salvador | $295.68M |
| 112 | Chad | $292.61M |
| 113 | Ghana | $289.40M |
| 114 | Niger | $287.28M |
| 115 | Sudan | $287.21M |
| 116 | Georgia | $286.02M |
| 117 | Gabon | $280.62M |
| 118 | South Sudan | $276.00M |
| 119 | Zambia | $251.16M |
| 120 | Mauritania | $194.48M |
| 121 | North Macedonia | $192.64M |
| 122 | Albania | $192.40M |
| 123 | Bosnia and Herzegovina | $178.11M |
| 124 | Mozambique | $140.20M |
| 125 | Kosovo | $128.69M |
| 126 | Zimbabwe | $117.39M |
| 127 | Kyrgyzstan | $116.04M |
| 128 | Madagascar | $109.76M |
| 129 | Eritrea | $105.32M |
| 130 | Mongolia | $91.98M |
| 131 | Tajikistan | $90.13M |
| 132 | Nicaragua | $88.34M |
| 133 | Benin | $75.25M |
| 134 | Montenegro | $74.07M |
| 135 | Somalia | $63.93M |
| 136 | Afghanistan | $49.53M |
| 137 | Moldova | $47.64M |
| 138 | Suriname | $41.89M |
| 139 | Central African Republic | $41.45M |
| 140 | Laos | $38.28M |
| 141 | Bhutan | $28.91M |
| 142 | Beliz | $19.33M |
| 143 | Sierra Leone | $19.33M |
| 144 | Liberia | $11.80M |
Read More Active Military Manpower By Country (Top 142 Countries)





































