Agriculture
Sugar Cane Production By Country (Top 92 Countries)
Sugarcane is a versatile and economically significant crop cultivated extensively in tropical and subtropical regions throughout the globe. It is grown predominantly for the production of Sugar, which is used in various food and beverage products. It is produced in 121 countries, and the annual global production has surpassed 120 million tonnes. Approximately 70% is derived from sugar cane, a tall vegetation with large stems primarily cultivated in tropical regions. The remaining 30% is derived from sugar beetroot, a root crop that resembles a large parsnip and is cultivated primarily in northern temperate zones.
Sugarcane production is a complex process involving planting, growing, harvesting, and processing the cane to extract its liquid, which is then further processed to produce different types of Sugar. The sugarcane industry is a significant source of income and employment for millions of people around the globe, particularly in developing nations where it is an important cash crop. However, environmental sustainability, labour practises, and economic competitiveness pose challenges for the industry.
Facts About Sugarcane Production:
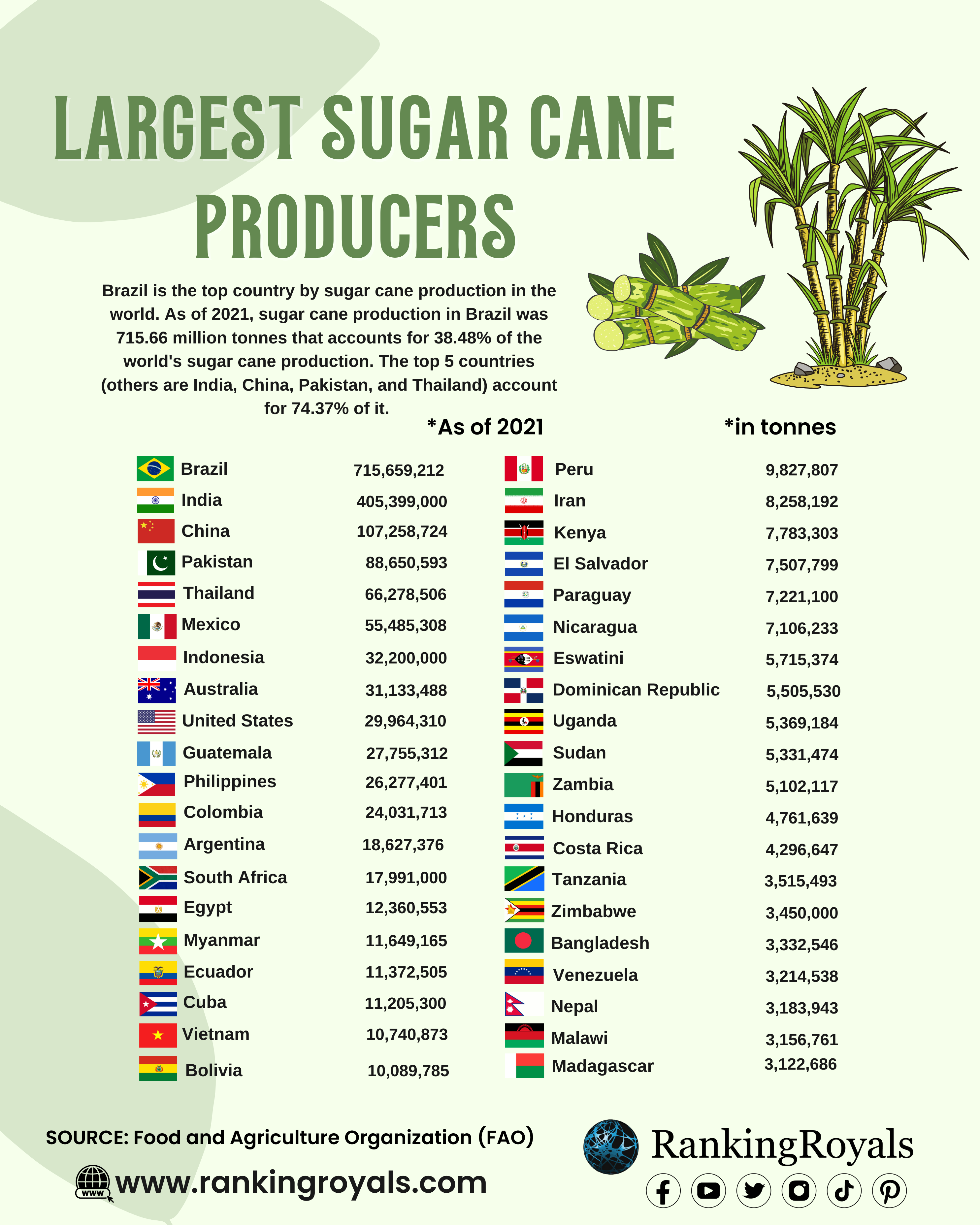
- Sugarcane is a tropical grass cultivated in over one hundred countries, with Brazil being the biggest producer, followed by India and China.
- Sugarcane is typically harvested after 12 to 18 months of growth in a muggy and humid climate.
- Ethanol, a renewable fuel that can be combined with petrol to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, is also produced from sugarcane.
- Both sugarcane and sugar beets are viable sources for sugar extraction. Sometimes, corn sugar is used as an alternative sweetener.
- China is the biggest producer of Sugar, but high tariffs impede its exports.
- Cane sugar makes up 80% of the market, but sugar beets are essential in more northern climes.
- Regardless of the reality that sugarcane production can be helpful for local economies, it can also have negative environmental effects such as deforestation, soil degradation, and water pollution.
Health Benefits of Eating Sugarcane:
Due to its high nutrient content, eating sugarcane can benefit your health in several ways. Sugarcane is a good source of calcium, potassium, magnesium, and iron, all essential nutrients. Sugarcane’s natural sugars can also give you a quick energy boost, making it an excellent snack for a quick pick-me-up. Sugarcane has a lot of fibre, which helps with digestion and can keep you from getting constipated. The potassium in sugarcane is also essential for controlling blood pressure and keeping the heart healthy. Sugarcane also has anti-inflammatory compounds called antioxidants.
Sugarcane is good for your health and can also help you stay hydrated. Sugarcane juice is a natural way to quench your thirst and can help replace fluids you lose when you work out or when it is hot outside. Also, sugarcane juice has a low glycemic index, so it does not quickly raise blood sugar levels like other sweets. Because of this, It is a good choice for people who have diabetes or are trying to keep their blood sugar under control. But it is important to remember that sugarcane should be eaten in balance since too much of it can raise blood sugar and make you gain weight.
Where is sugarcane grown?
The countries with the most sugarcane production have milder tropical climates. Extreme temperatures and a lack of precipitation result in drought, which reduces the amount of sugar cane that can be harvested. However, it is not all negative news. High temperatures can increase the sucrose yield from sugarcane, even though such conditions may result in much smaller cane plantations.
The continent with the most beet-producing regions in Europe. Inadequate weather conditions, such as flooding, frost, and precipitation, threaten the crop’s development.
How is Sugar made from sugarcane?
The production of Sugar from sugarcane is a multi-step procedure involving extraction, clarification, and crystallization. Sugarcane is first harvested and then transported to the sugar mill for processing. First, the sugarcane is crushed to extract its liquid, which contains sucrose, water, and other impurities. Next, the juice is clarified to eliminate impurities, including plant debris, proteins, and minerals. Typically, this is accomplished by adding lime and carbon dioxide to the liquid, which causes the pollutants to form solids that can then be extracted. The clarified juice is then boiled to remove extraneous water and concentrate its sugar content. The resulting syrup is then passed through a series of evaporators and crystallizers, where sugar crystals are formed and separated from the remaining syrup. The sugar crystals are then dried, graded, and packaged in various culinary and beverage products. To ensure a consistent and high-quality product, the entire process of producing Sugar from sugarcane must be carefully monitored and subject to stringent quality control.
Here is a list of the largest sugar cane producers by country, according to FAO:
| Rank | Country | Total Production (In Tonnes) |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Brazil | 715,659,212 |
| 2 | India | 405,399,000 |
| 3 | China | 107,258,724 |
| 4 | Pakistan | 88,650,593 |
| 5 | Thailand | 66,278,506 |
| 6 | Mexico | 55,485,309 |
| 7 | Oceania | 32,907,882 |
| 8 | Indonesia | 32,200,000 |
| 9 | Australia | 31,133,488 |
| 10 | United States | 29,964,310 |
| 11 | Guatemala | 27,755,313 |
| 12 | Philippines | 26,277,402 |
| 13 | Colombia | 24,031,713 |
| 14 | Argentina | 18,627,377 |
| 15 | South Africa | 17,991,000 |
| 16 | Egypt | 12,360,553 |
| 17 | Myanmar | 11,649,165 |
| 18 | Ecuador | 11,372,505 |
| 19 | Cuba | 11,205,300 |
| 20 | VietNam | 10,740,873 |
| 21 | Bolivia | 10,089,785 |
| 22 | Peru | 9,827,808 |
| 23 | Iran | 8,258,193 |
| 24 | Kenya | 7,783,303 |
| 25 | El Salvador | 7,507,799 |
| 26 | Paraguay | 7,221,100 |
| 27 | Nicaragua | 7,106,234 |
| 28 | Eswatini | 5,715,375 |
| 29 | Dominican Republic | 5,505,530 |
| 30 | Uganda | 5,369,184 |
| 31 | Sudan | 5,331,475 |
| 32 | Zambia | 5,102,118 |
| 33 | Honduras | 4,761,639 |
| 34 | Costa Rica | 4,296,647 |
| 35 | Tanzania | 3,515,493 |
| 36 | Zimbabwe | 3,450,000 |
| 37 | Bangladesh | 3,332,546 |
| 38 | Venezuela | 3,214,539 |
| 39 | Nepal | 3,183,943 |
| 40 | Malawi | 3,156,761 |
| 41 | Madagascar | 3,122,686 |
| 42 | Cambodia | 2,994,967 |
| 43 | Mozambique | 2,986,785 |
| 44 | Mauritius | 2,669,667 |
| 45 | Panama | 2,414,798 |
| 46 | DR Congo | 2,180,410 |
| 47 | Côte d'Ivoire | 2,102,319 |
| 48 | Belize | 1,893,663 |
| 49 | Laos | 1,885,346 |
| 50 | Nigeria | 1,498,023 |
| 51 | Haiti | 1,465,230 |
| 52 | Fiji | 1,417,000 |
| 53 | Senegal | 1,386,250 |
| 54 | Japan | 1,306,566 |
| 55 | Guyana | 1,280,703 |
| 56 | Cameroon | 1,230,923 |
| 57 | Ethiopia | 1,169,527 |
| 58 | Angola | 951,173 |
| 59 | Sri Lanka | 825,541 |
| 60 | Congo | 716,875 |
| 61 | Mali | 645,692 |
| 62 | Morocco | 613,254 |
| 63 | Taiwan | 594,724 |
| 64 | Burkina Faso | 506,733 |
| 65 | Jamaica | 499,218 |
| 66 | Uruguay | 457,000 |
| 67 | Niger | 445,294 |
| 68 | Chad | 410,102 |
| 69 | Papua New Guinea | 353,788 |
| 70 | Guinea | 316,681 |
| 71 | Gabon | 288,611 |
| 72 | Liberia | 275,988 |
| 73 | Somalia | 213,330 |
| 74 | Burundi | 200,746 |
| 75 | Ghana | 153,956 |
| 76 | Central African Republic | 129,698 |
| 77 | Rwanda | 97,991 |
| 78 | Barbados | 92,129 |
| 79 | Suriname | 86,950 |
| 80 | Benin | 82,856 |
| 81 | Sierra Leone | 81,323 |
| 82 | Bahamas | 61,991 |
| 83 | Afghanistan | 37,638 |
| 84 | Malaysia | 24,931 |
| 85 | Cabo Verde | 22,900 |
| 86 | Guinea-Bissau | 6,831 |
| 87 | Grenada | 5,618 |
| 88 | Dominica | 4,916 |
| 89 | Oman | 1,661 |
| 90 | Bhutan | 290 |
| 91 | Djibouti | 54 |
| 92 | Samoa | 12 |
Read More Global Motor Vehicle Sales By Country





































